Here’s a frightening truth: ecommerce is one of the most-targeted industries for cyberattacks, and the threat to online businesses is only increasing as criminals get more creative and use increasingly sophisticated technologies.
With this in mind, ecommerce businesses can approach cyber threats in one of two ways: put ecommerce website security decisions on the back burner and prioritize growth and disruption, or plan for these threats well before they inflict irreparable business and reputation damage.
The latter is a wiser approach, given that cybersecurity is more about what you can do than what you cannot. Planning is the key to minimizing cybercrime and mitigating the damage caused.
But what should this plan include? How can ecommerce businesses prepare for and protect themselves against advancing cyber threats?
Let’s explore.
How can your ecommerce store be attacked?
Cybercrime is evolving fast. Criminals are always trying to be one step ahead of their targets, and employ increasingly ‘creative’ methods to cause harm. So, how are ecommerce stores targeted?
The following are eight of the most commonly reported cyberattacks.
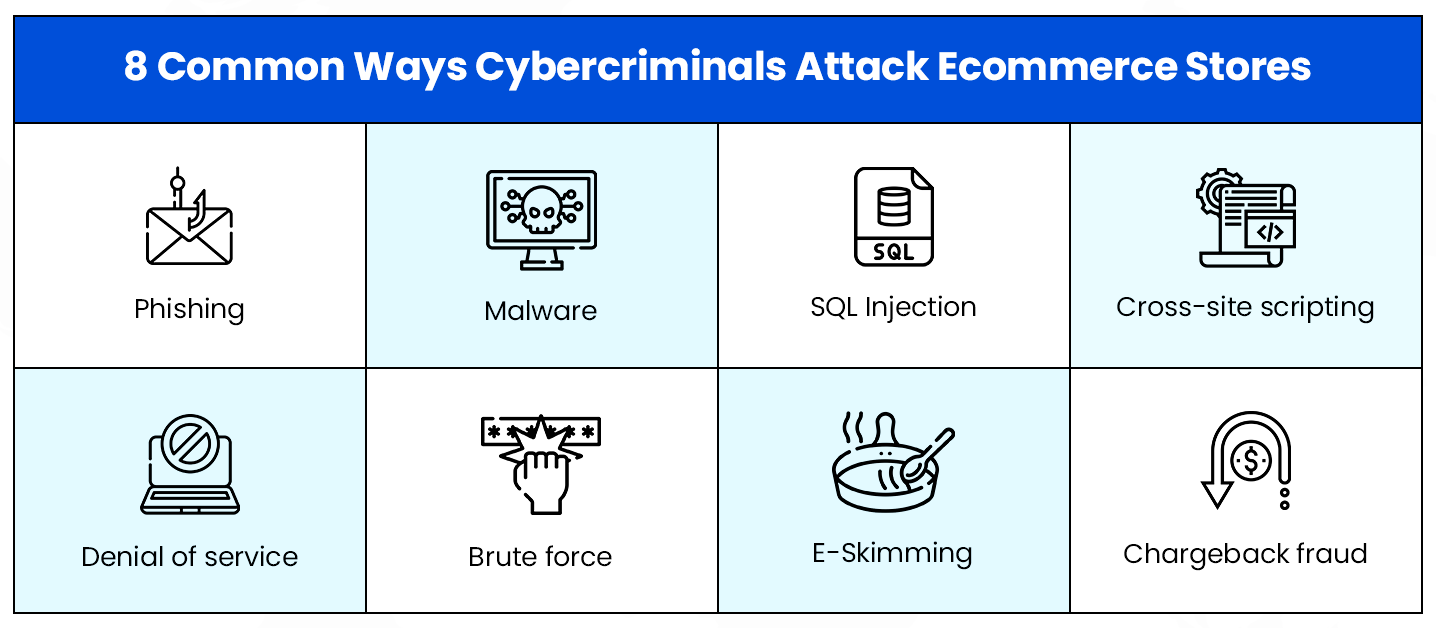
Let’s take a closer look at what these threats really are.
- Phishing: A form of social engineering, wherein cybercriminals pose as reputable sources and obtain sensitive information from unwitting victims.
- Malware: Malicious software in the form of a file or a code that is delivered over insecure networks and aims to infect digital systems and lockout website owners from their data and systems.
- SQL injection: Execution of malicious SQL statements to bypass security measures and retrieve the entire content of a web application’s SQL database.
- Cross-site scripting: Returning malicious code to users and compromising their interaction with a web application, exposing them to other forms of cybercrime.
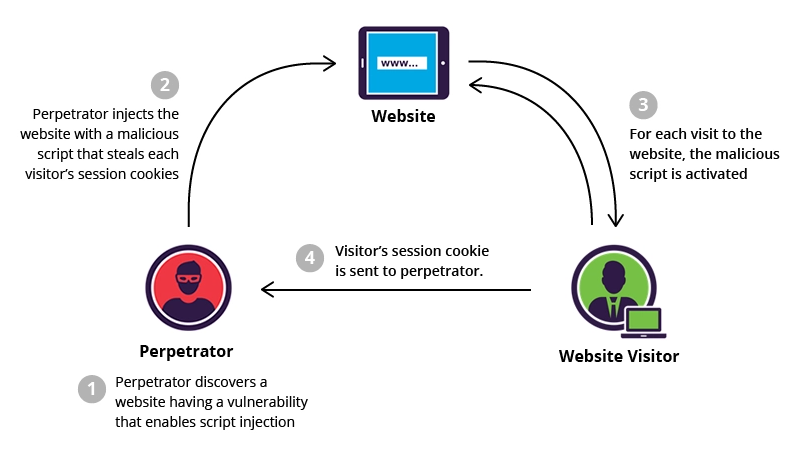
How cross-site scripting (XSS) is executed by cybercriminals. (Source: Imperva)
- Denial of service: Flooding a target server with transmission control protocol and user datagram protocol packets, overloading server capabilities shutting down networks so they can be hacked.
- Brute force: Using trial and error to crack passwords, encryption keys and login credentials. The process can be automated to try many combinations until the correct information is identified.
- E-Skimming: Introducing malicious code on online payment card processing pages to capture credit card and sensitive information, and sending the stolen data to another domain.
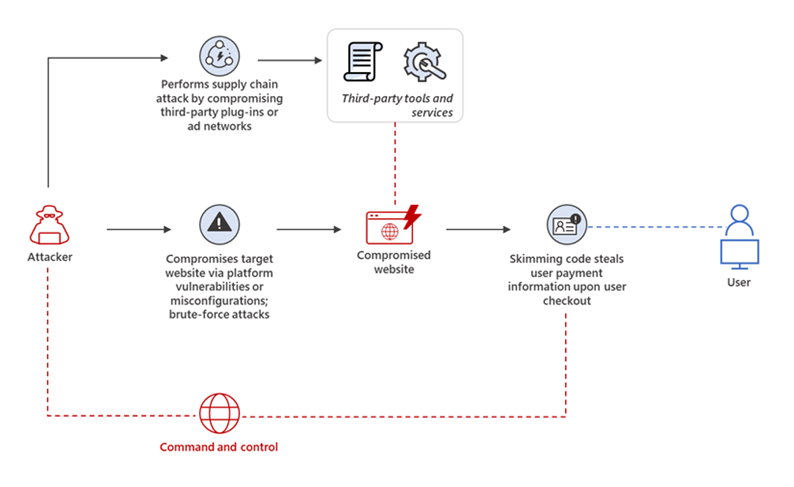
Attackers leverage system vulnerabilities to inject skimming scripts or conduct web-based supply chain attacks by finding vulnerabilities in third-party software or compromised ad networks. (Source: Microsoft)
- Chargeback fraud: When legitimate customers make a purchase from your website but then dispute the charge with their bank and essentially cyber-shoplift from your store.
What are the best practices to secure your ecommerce website?
In our experience, organisations can take ten initiatives towards successfully strengthening their cybersecurity infrastructure against most threats.
1. Ensure regulatory compliance
While simply adhering to cybersecurity compliances may not be enough to holistically protect your digital store, it’s a step in the right direction to protect the integrity and availability of your data.
To ensure that you’re complying with requirements imposed by law, regulatory bodies or private industries, follow these steps.

2. Conduct thorough security audits
When it comes to web application security, prevention is better than cure—especially for ecommerce applications.
To reduce susceptibility to cybercrime, digital store owners must conduct thorough manual and automated security audits and make adjustments that include:
- Updating scripts and applications
- Ensuring that IP and domain continue to remain clean
- Using strong passwords for accounts, dashboards and servers
- Conducting regular data cleansing to update information that is incomplete, irrelevant, incorrect, poorly formatted, or duplicated.
- Encrypting your entire web application using cryptographic network protocols.
3. Create data backups regularly
Regular data backups for ecommerce websites, while generally a good practice, also contribute to enhancing the security of your store. Cyberattacks can corrupt your data and render it unsalvageable. To prevent loss of data, restore website operations quickly and serve your customers free of interruptions and downtime, regular data backups are a must.
High-priority items that you must backup include the following.
- Critical website codes
- Database
- Content files
- Settings and configurations
- Layouts and themes
4. Use secure hosting services
Features and price are important considerations while choosing a web hosting service, but low prices and a wide range of features must not come at the cost of security. When choosing a web hosting provider, look out for the following security features:
- Automated and regular website backup and data retrieval mechanisms
- Secure Socket Layers (SSL) availability, configuration, and support
- Secure handling of regular software updates using the latest versions of scripts
- Valuable Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) prevention and mitigation protocols and a content delivery network (CDN) partnership
- Automated, remote and regular malware scanning and detection that aids rapid isolation of software infections.
Also Read: Hiring a BigCommerce Development Agency
5. Conduct vulnerability scans
Vulnerability scans and assessments can help you plug holes in your cybersecurity design before hackers can exploit them. Organisations must regularly conduct systematic checks of networks, applications, hardware, and the entire IT ecosystem. They must:
- Define the full scope of vulnerability testing and establish a concrete methodology
- Conduct manual and automated vulnerability scans, assigning severity levels to the weaknesses identified through risk ratings and scores.
- Treat vulnerabilities through fresh security patches, product updates, real-time antivirus software and remote firewall installation.
- Explore advanced technologies such as predictive artificial intelligence and automated malware engines to minimize vulnerabilities.
6. Secure the online payments process

Creating simple and secure checkout processes can not only prevent cybercrime but also reassure your customers that their money won’t be stolen. For this, ecommerce companies must:
- Match the buyer’s IP address with their billing address to verify that the customer is the cardholder.
- Encrypt and authenticate data using security protocols like SSL and TSL.
- Convert sensitive payment information into a string of random numbers to transport information safely. This is also called tokenization.
- Implement 3D Secure to authenticate transactions and reduce fraudulent chargebacks.
- Request for the Card Verification Value (CVV) to validate online payments.
Check out: Ecommerce Development Company
7. Create a strong customer authentication system
An important step towards overcoming and preventing specific attack vectors is setting up a foundationally secure customer authentication system. For this, some best practices ecommerce businesses can explore include:
- Enabling passwordless authentication.
- Implementing single sign-on and federated login.
- Securing the account recovery process and using safe authentication libraries.
- Implementing two-factor authentication and mutual authentication.
- Leveraging rate limiters in conjunction with CAPTCHAs to count failed authentication attempts and block user access temporarily.
- Enforcing password strength by using strength checkers and disallowing vulnerable passwords.
8. Protect against chargeback fraud
To cut down on customers charging back transactions erroneously or intentionally, ecommerce companies can take the following steps:
- Ensure that your charges are notated clearly and descriptively on your customers’ bank statements.
- Make use of order tracking numbers as proof of delivery in the case of fraudulent chargebacks.
- Block high-risk customers from transacting on your ecommerce website.
- Ensure that all sales and fulfilment process issues are resolved from your end.
- Ask banks and credit card companies to provide detailed chargeback codes for chargebacks initiated against your account.
9. Educate customers and employees
Your employees handle your ecommerce operations. It would be prudent to educate them on potential cybersecurity threats, so they can be sufficiently prepared to identify and even tackle these threats and bring them to the attention of relevant authorities.
Your customers must also be alerted to potential cyber frauds and educated on how to prevent them, especially during peak spending seasons such as the holidays, when cybercriminals are most active.
10. Look out for cybersecurity red flags
The most effective way to prevent falling into cybercrime traps is to be alert to social engineering and process red flags. These include:
- Incorrect domains and URLs suspiciously made to look familiar.
- Suspicious emails requiring you to transfer money or authorize transactions you don’t recognize.
- Insufficient budget allocation for cybersecurity measures.
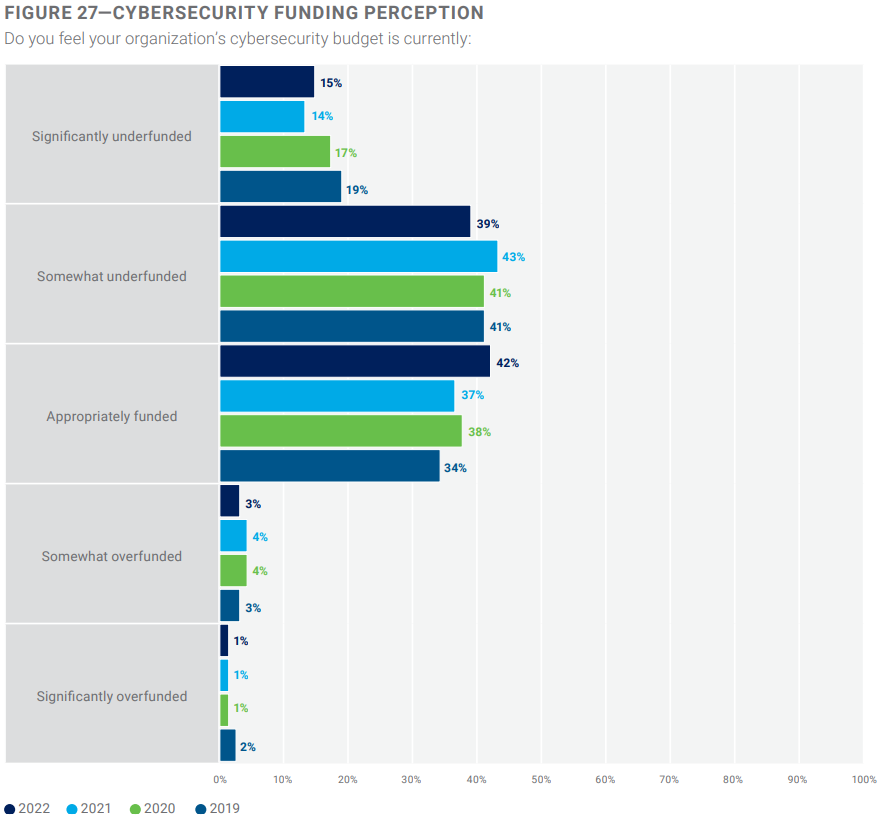
According to a report by the Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA), 1 out of 2 cybersecurity professionals believes that their organization’s cybersecurity budget is underfunded.
- An inordinately high amount of unfiltered spam emails.
- Irregular security audits and increased cybercrime incidents.
- Lack of firewall, encryption, and antivirus business solutions.
- Unclear security policies and untrained staff.
Leaders must be prepared for evolving threats
Cyber threats are increasing and evolving—between 2020 and 2021, there was an unbelievable 1070 percent increase in ransomware attacks. According to Microsoft data, cybercrime supply chains are maturing, and committing a digital crime is becoming increasingly easier.
As new, more sophisticated threats arise, businesses and IT leaders must explore key cybersecurity considerations, including the implementation of Identity and Access Management and zero-trust infrastructure, enhancing cloud and supply chain security through automation, shifting to a multidisciplinary approach to risk management, and shifting mindsets from cost and speed to efficacy of cybersecurity systems.
Strong cybersecurity can help your business thrive, even in times of uncertainty. Challenges will exist and new ones will emerge, but leaders must stay resilient and fight cyber threats with speed and agility.
Read Next: 20 Ecommerce Hacks to Supercharge Your Growth Strategy