Cloud computing shares a significant percentage of overall IT expenditure. A survey suggests that by 2026, spending on public clouds will make up over 45% of total company IT spending. In addition, IDC predicts that cloud spending will rise by 2025. The above-mentioned statistics identify that businesses are majorly spending a considerable amount of funds from their budget on the cloud.
If cloud expenses are not carefully planned and managed well, they can quickly deplete your company’s budget. That’s why modern businesses must consider optimizing cloud costs. Cloud cost optimization can avoid wasting up to one-third of the IT budget. By utilizing efficient strategies and technologies, businesses may more effectively manage their cloud resources, minimize expenses, and align their cloud spending with their objectives.
Organizations can reduce costs significantly, optimize operations, and manage their cloud resources strategically by utilizing the below-mentioned approaches. Adopting these strategies helps businesses make informed decisions and avoid over-cloud spending, which improves their operational agility. Are you also overspending on cloud solutions? This blog will give you eight significant ways to optimize cloud costs.
Why is Cloud Cost Optimization Important?
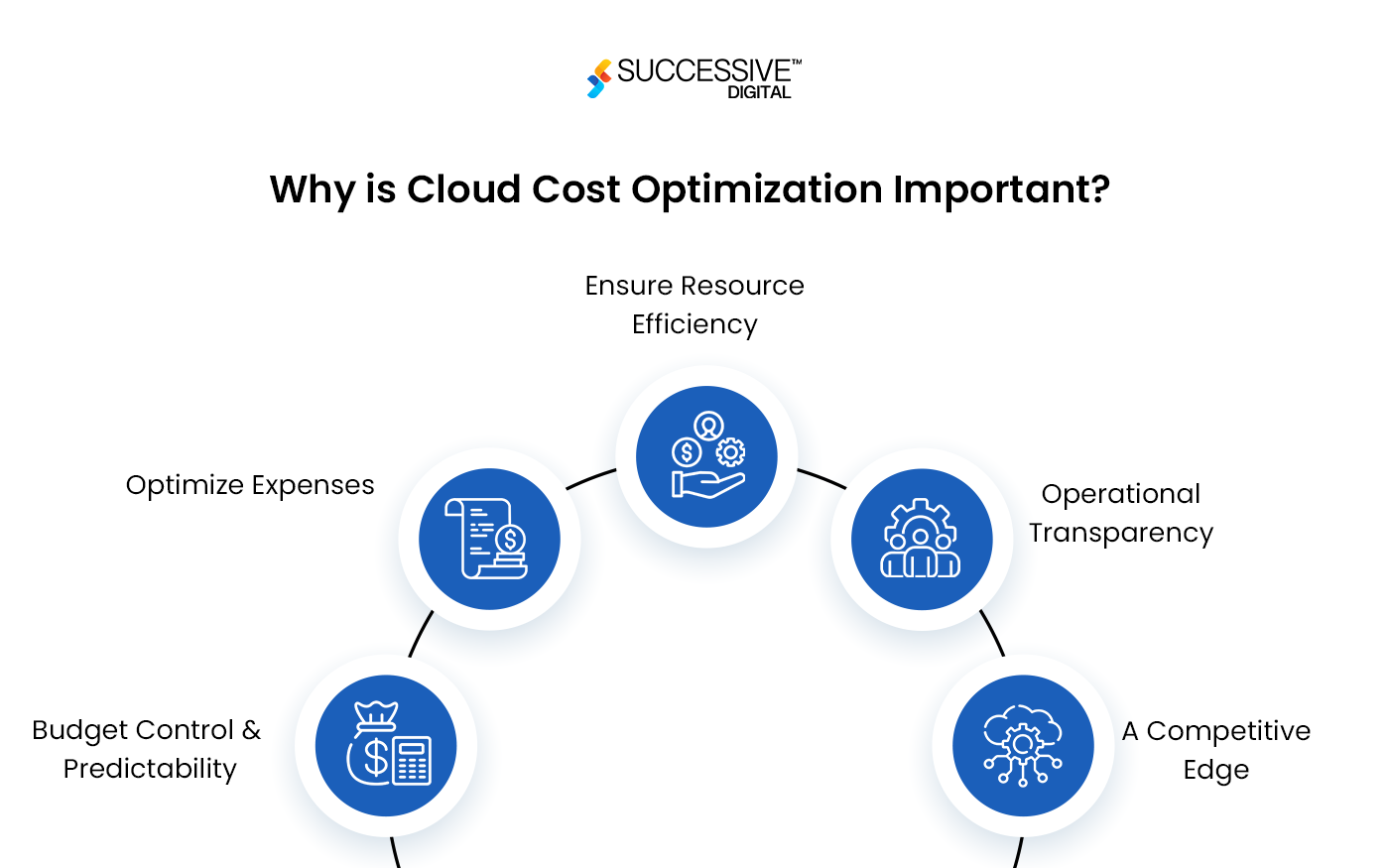
According to a Hashicorp study, over one-third of businesses had an annual cloud computing spend of over $2 million. At the same time, 51% are concerned about cloud costs, 39% believe their business has spent too much on the cloud in the last year, and executives think up to 20% of their cloud investment is wasted. Cloud cost optimization is dynamic, and it is crucial to adapt to changing application requirements and cloud price and service options. Because of the vast complexity of cloud settings, cloud cost optimization necessitates extensive data, analytics, and automation. Here’s why cloud cost optimization is essential:
- Budget Control & Predictability
A well-optimized cloud budget is predictable. With solid cost control mechanisms, you can precisely anticipate your cloud expenditure, avoiding surprises and allowing for more strategic planning.
- Optimize Expenses
Without proper control, cloud costs can become a budget black hole. Prioritizing cloud cost optimization allows you to avoid needless spending, freeing up funds for other essential business areas such as product development and hiring.
- Ensure Resource Efficiency
Effective cloud cost optimization entails right-sizing your resources, avoiding overprovisioning, and paying for wasted capacity. You’ll pay for what you require when you need it.
- Operational Transparency
Cloud cost optimization and cost reporting improve visibility into where and how your cloud budget is spent. This better understanding can improve accountability while harmonizing your technology and business objectives.
- A Competitive Edge
With resources used efficiently and expenses under control, you can concentrate on innovating as an organization, eventually reducing your time to market—product roadmap prioritization or investigating marketing ideas that attract customers.
8 Major Ways to Build a Robust Cloud Cost Optimization Strategy
- Capacity Planning
Estimating how many resources will be required to meet an application’s or system’s present and future demands is known as capacity planning. It serves as a proactive measure to mitigate the risks associated with either under or over-provisioning resources. By ensuring that their IT infrastructure aligns with operational needs and growth objectives, companies can optimize performance and maintain operational efficiency. Capacity planning helps companies make well-informed decisions regarding resource allocation, scalability, and optimization by examining past data, trends, and other variables.
Despite the flexibility of cloud services allowing for rapid scaling, organizations often find themselves paying for unused capacity. IT departments must ensure sufficient capacity to manage unforeseen load variations and traffic spikes, but it’s imperative to avoid overspending on pointless resources.
Selecting appropriate cloud resources for your workload is an important component of capacity planning. With a wide range of compute instance configurations available, companies can match the processing power, memory, storage, and performance requirements of each application. However, there is a risk of overprovisioning by providing more resources than required, resulting in higher expenditures without equivalent advantages.
Additionally, autoscaling helps enterprises avoid paying for unutilized cloud capacity. Cloud vendors like AWS provide native services with autoscaling capabilities. Designing and optimizing cloud applications with an autoscaling configuration enables them to leverage the elasticity of cloud computing. Autoscaling with elasticity eliminates manual intervention, making resource allocation seamless and effortless. Furthermore, it prevents resource waste by scaling down systems during periods of low demand.
Consider the cost when setting up the autoscaling parameters. For example, set performance constraints for lower-priority tasks that don’t call for significant scaling. Additionally, serverless computing can also help with scaling problems, acute planning is required to prevent runaway expenses.
- Set Budgets
Cloud is no doubt one of the best technologies to utilize for business operations. But to keep the financial balance, it’s very important to determine the budget and set prior expectations. This budget may change depending on your company’s needs. A well-defined financial plan is essential for organizing overall expenditures and minimizing expenses.
The key to successful cost management is encouraging communication at every organizational level. Companies can proactively control costs and optimize resource allocation by assuring agreement about project objectives and expenditure restrictions between engineering teams, executives, and product leadership.
Comprehending cloud billing and usage trends enables businesses to plan ahead and reduce unanticipated expenses. In contrast to traditional on-premises IT costs, which can need large upfront investments, cloud computing costs are defined by usage-based pricing that varies on a monthly basis and monthly membership fees.
As a result, businesses need to set governance standards that balance IT expenses and performance without limiting the flexibility that cloud computing provides. In-depth cooperation between IT and finance is necessary to achieve this. Thus, businesses must consider involving IT team members, such as developers, systems operators, and security experts, in their conversations on cloud budgeting.
- Limit Data Transfer Fees
Data Transfer Costs are the costs of sending data across cloud services, regions, or accounts. These fees vary depending on the cloud provider, the amount of data transported, and the regions involved.
Some cloud providers offer free data transfers in specific circumstances, such as inbound transfers or transfers within the same region.
Transferring data to and from a public cloud might be costly. Cloud companies charge data costs for moving data outside their systems or between regions. To save on cloud charges, avoid unnecessary data transfers.
Analyze the transfer fees offered by your cloud provider first. Next, modify your cloud architecture to minimize the required data transfers. To avoid hurdles, you could transfer on-premises apps that regularly request data hosted on the cloud into the cloud.
Analyze the costs associated with the transfer techniques to speed up and secure data transfers between private data centers and the cloud. You can evaluate the expenses of purchasing a physical transfer device like an AWS Snowball or an Azure Data Box against the prices of utilizing a dedicated network connection service like AWS Direct Connect, Google Cloud Interconnect, or Azure ExpressRoute.
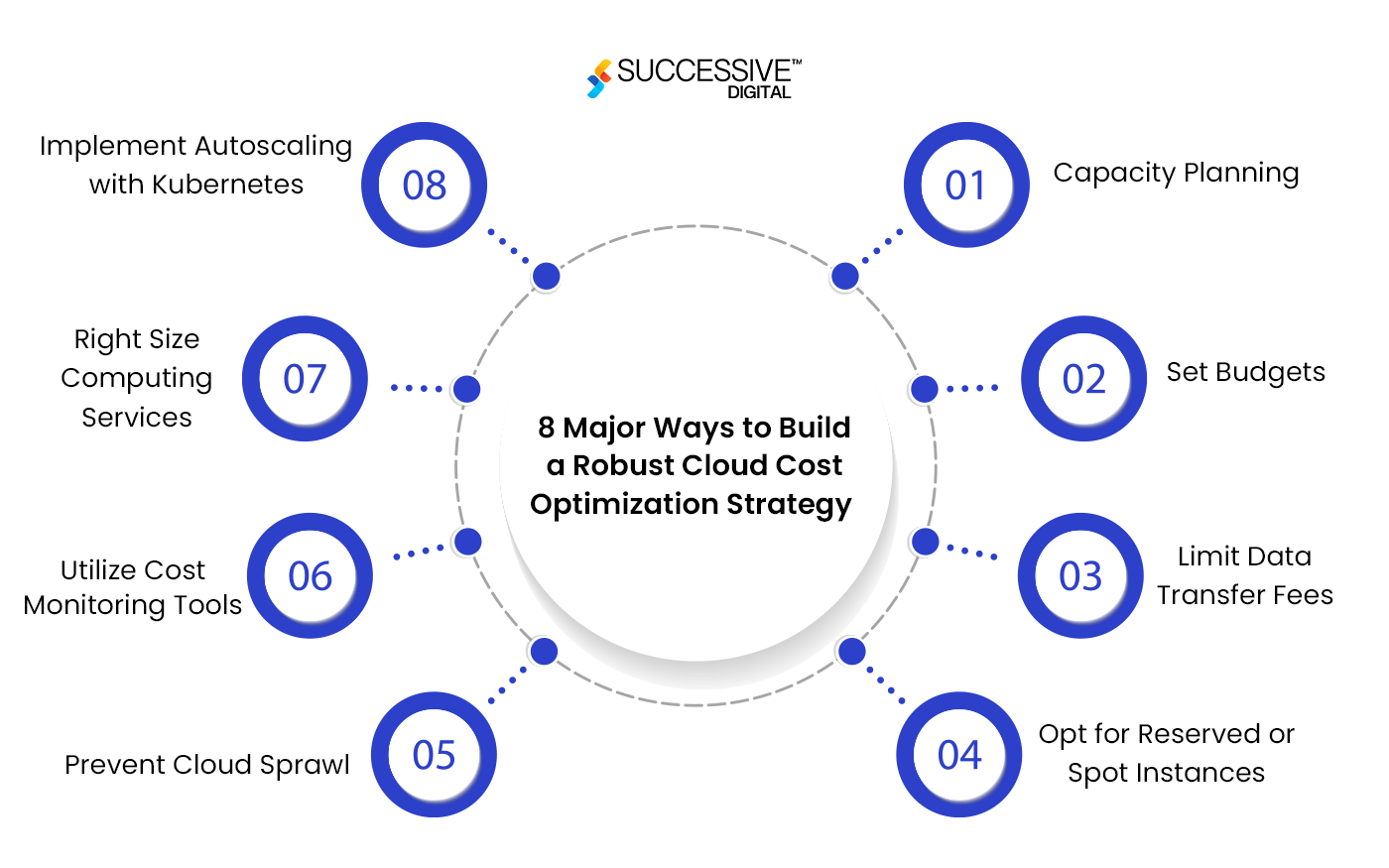
- Opt for Reserved or Spot Instances
Spot and reserved instances differ mostly in terms of availability and cost. Spot occurrences carry a risk of disruption even though they can result in large cost reductions. On the other hand, reserved instances guarantee resource availability for long-term obligations. Use the below-mentioned structures as per the requirement:
Spot Instances: With Google Cloud Preemptible VMs, Azure Spot VMs, Amazon EC2 Spot Instances, and Google Spot VMs, developers can obtain spare capacity at a much-reduced cost. These pricing methods determine the savings based on the kind of resource purchased and the price at the moment of purchase. These instances may have sudden terminations based on the region’s overall capacity demands. Stateless workloads, batch processes, and other tasks that can withstand interruptions are their ideal uses.
Reserved Instances: Reserved instances allow organizations to save money on cloud resources by offering an upfront commitment to use a specific capacity over one to three years. Reserved instances can save you up to 80% over on-demand cases, depending on the platform and other factors. With Amazon EC2 Reserved Instances (RIs), Azure Reserved VM Instances, and the Google Cloud Committed Use program, all the leading cloud providers give this pricing option. AWS’s savings plans offer similar savings and greater usage flexibility than regular EC2 RIs. The ideal workloads for reserved instances are those with steady, predictable capacity.
- Prevent Cloud Sprawl
Cloud sprawl is the uncontrolled utilization of a company’s cloud services, instances, and resources. It is unplanned but known as a byproduct of an organization’s rapid cloud services and resource expansion. Disorganized development exacerbates cloud sprawl, which can have profound operational and security implications.
Cloud bill spikes can be attributed to cloud sprawl, the unchecked usage of cloud resources. Organizations continue to pay for cloud services when they don’t get rid of them when they no longer fit into their overall plan.
Storage instances can accumulate, especially if they are not correctly linked to compute instances or are utilized for data protection. Often, unused storage linked with discontinued cloud server instances is overlooked. It is critical to discover and eliminate redundant storage instances in compliance with the organization’s data retention policy.
To handle cloud sprawl, it is critical to have clear insight into the cloud environment by utilizing monitoring tools for both infrastructure and applications. Establishing business policies for the prompt decommissioning of cloud services and enabling automatic provisioning for obsolete applications can assist reduce sprawl. Also, it is essential to monitor cloud contracts and bills to determine whether your company is paying for services that are no longer needed.
- Utilize Cost Monitoring Tools
An efficient cost management approach necessitates appropriate budgeting tools. Cloud is so vast that if you do not utilize efficient tools you may end up in a mess.
AWS provides several cost-monitoring tools. AWS Cost Explorer examines your previous spending (up to 13 months) and projects your cloud expenses for the following three months. Another alternative, AWS Budgets, employs configurable alarms to notify administrators when expenditure exceeds a predetermined threshold. It can also automatically limit resources to lower cloud costs.
Microsoft Cloud users may keep track of their spending with Azure Cost Management + Billing. This collection of tools monitors expenditures across individual Azure services, estimates future bills, and notifies customers when they exceed budget. Similarly, Google Expense Management helps Google Cloud Platform users spot expense spikes and create spending reports for cost minimization.
In addition to cloud-based options, third-party cost monitoring tools assist firms in making informed expenditure decisions. Several systems track spending across cloud resources and recommend where to decrease costs. Other third-party cloud cost monitoring and management applications include CloudZero and Densify.
- Right Size Computing Services
Right-sizing is selecting instance types and sizes that meet your workload’s performance and capacity requirements at the lowest available cost. It is also the process of reviewing deployed instances and discovering possibilities to delete or shrink without sacrificing capacity or other requirements, resulting in decreased costs.
To properly right-size your cloud computing services, first analyze your workloads. Assess their performance requirements and usage patterns to optimize computing resources optimally. Experiment with various configurations, including instance sizes and kinds, to determine the best fit for each task.
Use heatmaps to visually display your company’s computing demand over time, allowing you to discover cost centers and allocate resources accordingly. Utilize load balancing to distribute workloads evenly across resources, preventing overuse and underuse. Finally, remember that right-sizing is an ongoing process; monitor and modify your resources as workloads change to generate considerable long-term cost reductions.
Want to minimize your cloud expenses- Contact us today!
- Implement Autoscaling with Kubernetes
Scaling on demand is one of the most significant benefits of establishing a cloud-first business. However, manually managing resources can be difficult, resulting in over-provisioning and increased expenditures. Autoscaling has the potential to save costs while also allowing for optimal resource optimization.
Autoscaling enables you to automatically alter the number of computer resources based on actual consumption. Autoscaling is especially beneficial for unpredictable and mission-critical workloads. Instead of leaving resources idle during low-usage periods or exceeding capacity during high-usage periods, it guarantees you consume the appropriate amount in the proper time.
One option for enabling autoscaling is Kubernetes, an open-source container orchestration system known for automating application deployment, scaling, and management. Kubernetes has several methods for good autoscaling:
- Cluster Autoscalers (CA)
- Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA).
- Vertical Pod Autoscalers (VPA)
While Kubernetes is available on other cloud platforms, Successive offers a managed Kubernetes solution. This service eliminates the complexity of setting up and managing a Kubernetes environment, allowing you to focus on deploying and scaling your applications.
Build Your Cloud Cost Optimization Strategy with Successive Digital
The public sector organization in the energy and electricity sector aimed to update its technology and infrastructure to handle incoming traffic from different internet sources effectively. The main business goal was moving from a monolithic data center to a more secure and flexible cloud-based architecture with automation to expedite operations. They aim to create a stable environment to manage scalable workloads while balancing performance and cost safely. The client realized it needed to change its IT administration to offer online services and handle growing traffic because their traditional on-premise infrastructure was not scaling well. Ultimately, they wanted to improve the customer experience by using omni-channel communication.
By setting up an AWS landing zone, creating the groundwork for cloud migration, and guaranteeing a dependable environment for safe and scalable application operations, Successive Digital offered a holistic solution.
The solution enabled cost control, faster delivery and deployment times, and seamless interaction with the current infrastructure by utilizing AWS DevOps capabilities, including Code Build, Code Deployment, and Code Pipelines. The key features were
- standardized MySQL deployment,
- backup and disaster recovery procedures,
- automated administrative chores, and
- multi-AZ deployment for increased resilience.
With an impressive 80% improvement in deployment speed and a 20% reduction in cloud expenses, the implementation had a significant business impact and proved that the partnership was successful in helping the client achieve their digital transformation objectives.
Conclusion
Organizations seeking to minimize their cloud expenses must implement a comprehensive cloud cost optimization plan that includes the eight abovementioned best practices. Businesses can proactively control expenses without sacrificing performance by deploying Spot Instances and Low-Priority VMs, leveraging Reserved Instances and Savings Plans, and right-sizing resources. Cost control methods are enhanced through automation of workload management operations, resource organization through tagging and categorization, and the construction of solid cloud governance frameworks. Sustained cost reductions and operational efficiency are ensured by embracing cloud-native technologies and regularly tracking and optimizing cloud utilization.
FAQs - Cloud Cost Optimization
Yes, using a multi- or hybrid cloud strategy can help with cloud cost optimization. Multi-cloud refers to employing several cloud service providers, whereas hybrid cloud combines on-premises, private, and public cloud services. Organizations can save money using alternative cloud environments based on individual workload requirements and pricing variables.
Indeed. Running applications in less expensive areas enhances cloud cost optimization. Geographically based pricing models for cloud service providers are standard; certain countries have cheaper costs because of reduced energy costs, tax advantages, or competition. Enterprises can lower their total cloud costs without sacrificing availability or performance by smartly placing workloads in these economically advantageous regions.
Controlling and lowering cloud costs while preserving or enhancing performance, dependability, and security is known as cloud cost optimization or CCO. It entails examining how cloud computing is used, spotting inefficiencies, and implementing plans to maximize expenses without compromising operational goals. CCO includes a range of strategies, including implementing cloud governance policies, automating workload management, leveraging pricing structures, and rightsizing resources. Optimizing the use of cloud resources, reducing waste, and maximizing return on investment (ROI) in cloud infrastructure and services are the objectives of CCO.
The following are four cloud-based cost optimization pillars:
- Rightsizing ensures that resources are within and under-utilized by matching workload requirements.
- Constantly look for ways to reduce expenses by using strategies that include utilizing pricing models, automating procedures, and implementing effective structures.
- Adopting cloud-native architectures, services, and technologies to increase productivity, adaptability, and scalability while cutting expenses and operational overhead.
- Establish frameworks, guidelines, and governance controls to oversee cloud usage, ensure compliance, and maximize spending throughout the company.